Whey Protein vs. Plant-Based Protein for Muscle Growth: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Protein is the cornerstone of muscle growth, and for fitness enthusiasts, the choice between whey and plant-based protein can be pivotal. Each type of protein has its advocates and critics, often leading to heated debates in gym locker rooms and online forums. In this in-depth analysis, we’ll explore the science behind Whey Protein vs. Plant-Based Protein for Muscle Growth, unraveling the myths and presenting the facts to help you make an informed decision for your fitness journey.
Whether you’re pushing for that extra rep or seeking the best post-workout recovery, understanding the impact of your protein choice is key. So let’s dive into the world of proteins and discover which might give you the edge in building muscle and optimizing your health.
Understanding Protein and Muscle Growth
What is Protein?
Protein, one of the three macronutrients alongside fats and carbohydrates, is crucial for the body’s structural and functional purposes. It’s composed of amino acids, which are often referred to as the building blocks of life. There are twenty different amino acids that link together in various sequences to form proteins. Nine of these are considered essential, meaning our body cannot produce them on its own and we must obtain them through our diet.
How Does Protein Contribute to Muscle Growth?
Muscle growth, scientifically known as hypertrophy, is a complex process that involves more than just lifting weights. When we engage in resistance training, we create micro-tears in our muscle fibers. In response, our body repairs these damaged fibers through a cellular process where it fuses muscle fibers together to form new muscle protein strands or myofibrils. These repaired myofibrils increase in thickness and number to create muscle hypertrophy.
Protein plays a pivotal role in this repair process. After a workout, the body increases its rate of protein synthesis, utilizing the amino acids from protein to rebuild and grow the muscles. This is why protein intake is often emphasized for anyone looking to increase muscle mass and strength.
To truly understand the impact of protein on muscle growth, let’s delve into the specifics of whey and plant-based proteins.
Whey Protein: The Traditional Muscle Builder
What is Whey Protein?
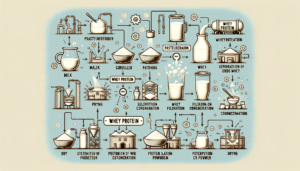
Whey protein is a high-quality, complete protein naturally found in milk. During the process of making cheese, enzymes are added to heated milk, causing it to separate into curds and liquid whey. The whey is then processed to remove fats and carbohydrates, leaving a concentrated powder rich in protein.
Benefits of Whey Protein for Muscle Growth
- Complete amino acid profile: Whey is a complete protein, providing all nine essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth and repair.
- High leucine content: Leucine is one of the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and plays a key role in promoting muscle protein synthesis.
- Fast absorption: Whey protein is absorbed quickly by the body, making it an ideal source of protein immediately after a workout for muscle recovery.
Potential Drawbacks of Whey Protein
While whey protein is a powerhouse for muscle growth, it’s not without its drawbacks. Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort due to lactose intolerance or a sensitivity to dairy-derived products. Moreover, whey protein production is tied to the dairy industry, which raises concerns about environmental sustainability and animal welfare.
To address these concerns, many companies now offer lactose-free whey protein options, and some are committed to sustainable and ethical practices.
Plant-Based Protein: The Emerging Contender
What is Plant-Based Protein?
Plant-based proteins are derived from various plant sources such as peas, rice, soy, and hemp. Unlike animal proteins, plant proteins can be incomplete, lacking one or more of the essential amino acids. However, by combining different plant-based protein sources, it’s possible to create a complete amino acid profile that supports muscle growth.
Can Plant-Based Protein Support Muscle Growth?
Recent studies, such as the one published in the journal “Nutrients,” suggest that plant-based proteins can support muscle growth effectively. The key is ensuring that the protein consumed contains all the essential amino acids in adequate amounts, which can sometimes require combining different plant protein sources.
Advantages of Plant-Based Protein
- Nutrient-rich: Many plant-based proteins come packed with additional nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Allergen-friendly: Plant-based proteins are often suitable for individuals with allergies or intolerances to dairy or other animal products.
- Sustainable: Choosing plant-based protein sources can have a lower environmental impact than animal-based proteins.
Disadvantages of Plant-Based Protein
Despite the advantages, there are challenges associated with plant-based proteins. They may have a lower rate of absorption compared to whey protein, and achieving a complete amino acid profile may require more effort in meal planning.
To address these challenges, it’s important to select a variety of plant-based protein sources and ensure adequate protein intake throughout the day.
Comparing Whey and Plant-Based Protein
Nutritional Showdown: Amino Acid Profiles

Amino acids are the critical factor when comparing whey and plant-based proteins. Whey protein is complete and rich in BCAAs, which are vital for muscle protein synthesis. Plant-based proteins, when combined correctly, can also provide a complete amino acid profile, but individual plant proteins often lack one or more essential amino acids.
To illustrate the amino acid profiles of whey and plant-based proteins, here is a comparison table:
| Amino Acid | Whey Protein | Plant-Based Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Leucine | High | Varies |
| Isoleucine | High | Varies |
| Valine | High | Varies |
| Lysine | High | Varies |
| Methionine | High | Varies |
| Phenylalanine | High | Varies |
| Threonine | High | Varies |
| Tryptophan | High | Varies |
| Histidine | High | Varies |
Digestibility and Absorption
Whey protein is renowned for its rapid absorption, making it a go-to for post-workout nutrition. Its high solubility and fast digestion rate allow amino acids to be quickly released into the bloodstream, facilitating muscle recovery and growth. Plant-based proteins, on the other hand, may have a slower digestion rate due to factors like fiber content or the presence of anti-nutritional factors. While slower digestion may not be ideal for immediate post-workout recovery, it can provide a sustained release of amino acids throughout the day.
Muscle Growth Outcomes in Studies
Research indicates that the source of protein—whether from whey or plants—is less important than the total amount of protein consumed in relation to muscle growth. A study in the “Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition” found that as long as the diet provides enough protein to meet the athlete’s needs, muscle growth can be supported by either whey or plant-based protein sources.
It’s also worth noting that individual responses to different protein sources may vary. Some individuals may experience better muscle growth with whey protein, while others may respond equally well to plant-based proteins. Experimentation and personal preference play a role in finding the optimal protein source for muscle growth.
Whey vs. Plant-Based Protein for Fat Loss
Both whey and plant-based proteins can aid in fat loss by promoting satiety and preserving lean muscle mass. Whey protein, in particular, has been shown to have a slight edge in promoting fat loss due to its ability to increase energy expenditure and reduce appetite.
A study published in the “Journal of the American College of Nutrition” compared the effects of whey protein and soy protein on body composition during a calorie-restricted diet. The results showed that both protein sources were effective in preserving lean mass, but whey protein led to a greater reduction in body fat.
Practical Considerations for Fitness Enthusiasts
How to Choose the Right Protein for Your Diet
Choosing between whey and plant-based protein should be based on individual dietary needs, preferences, and fitness goals. Consider factors such as digestibility, amino acid profile, and any dietary restrictions you may have.
If you’re lactose intolerant or have dairy allergies, plant-based proteins may be a better choice. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a complete protein source with a high leucine content and fast absorption, whey protein could be the optimal option.
How to Optimize Protein Intake for Muscle Growth
To optimize muscle growth, prioritize protein intake around workouts and aim for a daily intake of 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This will support muscle repair and growth, especially when combined with resistance training.
Distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day, rather than consuming a large amount in a single meal, can also enhance muscle protein synthesis.
Combining Whey and Plant-Based Proteins
Combining whey and plant-based proteins can provide a broad spectrum of amino acids and nutrients. For example, mixing whey protein with a plant-based protein like pea or rice can enhance the overall amino acid profile and support muscle growth.
Experiment with different combinations to find what works best for you. Consider incorporating protein blends that combine multiple protein sources, offering the benefits of both whey and plant-based proteins.
Overcoming the Challenges of Plant-Based Muscle Building
How to Get Enough Protein on a Plant-Based Diet

A well-planned plant-based diet can provide sufficient protein for muscle growth. Focus on diverse protein sources like legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, and consider supplementing with a complete plant-based protein powder if necessary.
To ensure you’re meeting your protein needs, here are some examples of plant-based protein sources and their protein content per serving:
- Lentils (1 cup cooked): 18 grams of protein
- Quinoa (1 cup cooked): 8 grams of protein
- Chickpeas (1 cup cooked): 15 grams of protein
- Tofu (1/2 cup): 10 grams of protein
- Chia seeds (2 tablespoons): 4 grams of protein
By incorporating a variety of these plant-based protein sources into your meals and snacks, you can meet your protein requirements for muscle growth.
Building Muscle on a Plant-Based Diet
Building muscle on a plant-based diet is entirely achievable. Ensure you’re consuming enough calories to support muscle growth, and pay attention to protein timing, particularly post-workout when muscle repair and growth are most active.
In addition to protein, other nutrients like carbohydrates and fats are essential for muscle growth. Incorporate whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats into your diet to provide the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal muscle development.
Conclusion
In the quest for muscle growth, both whey and plant-based proteins have their place. Your choice should align with your dietary preferences, ethical considerations, and fitness goals. By understanding the nuances of each protein source, you can tailor your nutrition to support your muscle-building journey effectively.
Remember, the key to muscle growth is not solely dependent on protein type but also on total protein intake, resistance training, and overall nutrition. Experimentation and finding what works best for your body and lifestyle are crucial.
FAQs
Q: Can I build muscle with plant-based protein?
A: Yes, you can build muscle with plant-based protein. As long as you consume a variety of plant-based protein sources that provide all the essential amino acids and meet your daily protein needs, muscle growth can be effectively supported.
Q: Is plant protein better than animal protein for building muscle?
A: Both plant and animal proteins can effectively support muscle growth when consumed in adequate amounts. The key is ensuring you meet your protein needs and maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods.
Q: Should I use plant protein or whey protein?
A: The choice between plant protein and whey protein depends on various factors, including dietary preferences, allergies, and ethical considerations. Consider your individual needs and goals to determine which protein source aligns best with your lifestyle.
Additional Resources
For those who want to explore the research and evidence further, here are some additional resources:
- A Novel Plant-Based Protein Has Similar Effects Compared to Whey Protein on Body Composition, Strength, Power, and Aerobic Performance in Professional and Semi-Professional Futsal Players: This study, conducted with high-level futsal players, found no significant differences in muscle growth, strength, power, or aerobic performance between participants consuming a novel plant-based protein or whey protein, suggesting both can be equally effective when providing sufficient essential amino acids.
- Animal Protein versus Plant Protein in Supporting Lean Mass and Muscle Strength: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: This meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials concluded that both animal and plant-based protein sources can effectively support lean mass and muscle strength gains in resistance-trained individuals. The key factor seems to be adequate protein intake (1.6-2 g/kg body weight) and proper training, not the protein source itself.
- The Role of Protein in Muscle Mass Gain: This review highlights the crucial role of protein intake, regardless of source, in muscle mass gain when combined with resistance training. It also emphasizes the importance of choosing high-quality proteins with complete amino acid profiles, like whey or soy protein, for optimal muscle-building effects.
By providing these additional resources, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their protein choices and optimize their muscle growth journey.
Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or supplementation routine.




